inhibitors of electron transport chain ppt|(PPT) Chapter 6 Electron transport chain and : Manila It discusses key concepts like the Q-cycle, shuttle systems that transport cytosolic NADH into mitochondria, uncoupling proteins, and various inhibitors that . zoo roulette game tricks | zoo roulette game tricks | zoo roulette 600 se 4100 jit liyahelo friend welcome to my new videoApp Link 🔗 👇Rummy Mate :-http://b.
inhibitors of electron transport chain ppt,This document discusses inhibitors and uncouplers of the electron transport chain (ETC). It provides examples of several types of inhibitors that block .
The electron transport chain (ETC) transfers electrons from electron donors like .It discusses key concepts like the Q-cycle, shuttle systems that transport cytosolic . The electron transport chain (ETC) transfers electrons from electron donors like NADH to electron acceptors like oxygen via redox reactions across the inner . It discusses key concepts like the Q-cycle, shuttle systems that transport cytosolic NADH into mitochondria, uncoupling proteins, and various inhibitors that .Colby College offers a PowerPoint presentation on the electron transport chain, a crucial process in cellular respiration and energy production. Learn about the components, .
Cellular respiration involves four phases: glycolysis, the preparatory reaction, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Electron transport chains are biochemical reactions that produce ATP, which is .inhibitors of electron transport chain pptWhat change would you expect in ATP concentration in the cell? A. Decrease in [ATP] B. Increase in [ATP] C. No change D. ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN • Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through an electron transport chain to oxygen, which is reduced to water. • This is a multi-step redox process that .(PPT) Chapter 6 Electron transport chain and Objectives. To understand the concept of inhibitors and uncouplers. To understand the inhibitors of respiratory complexes. Inhibitors of the ATP synthesis. Background .

A common inhibitor of the ETC is carbon monoxide; this will bind to Complex IV and therefore halt the passing of electrons. Without electrons passing .

What Are the Reduction Potentials for the Electron Transport Chain? How Are the Electron Transport Complexes Organized? What Is the Connection between Electron Transport .Inhibitors of Electron Transport Chain oxygen which stops the further passage of electron through the electron transport chain. As a result, the person is deprived of energy to carry out the many numerous processes that sustain life and the person dies. Carbon monoxide: It is a respiratory inhibitor which blocks the complex IV of the .
The electron transport chain is comprised of a series of enzymatic reactions within the inner membrane of the mitochondria, which are cell organelles that release and store energy for all physiological needs. As electrons are passed through the chain by a series of oxidation-reduction reactions, energy is released, creating a gradient of .
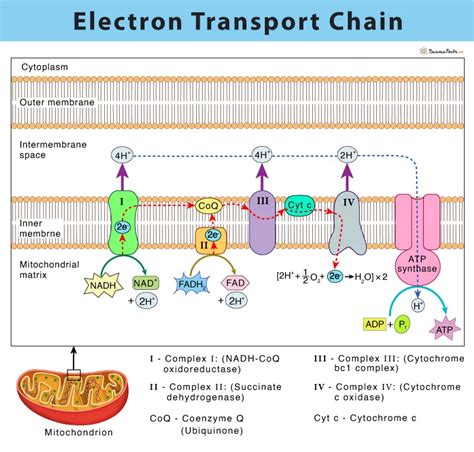
Electron Transport Chain - Download as a PDF or view online for free . Factors like substrate concentration and inhibitors can also affect an enzyme's reaction rate. Recommended. AS Level Biology - 3) Enzymes. AS Level Biology - 3) Enzymes. Arm Punyathorn . all about Enzymes 1234567891011121314.ppt. all about Enzymes . Cyt c passes electrons to Complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase; labeled IV), which uses the electrons and hydrogen ions to reduce molecular oxygen to water. Together, oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation account for most of the ATP synthesized by most organisms most of the time. The electrons flow from .
1) The electron transport chain is the final stage of cellular respiration that occurs in the mitochondria. 2) It involves a series of protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transport electrons and pump hydrogen ions across the membrane, building up a proton gradient. 3) The flow of hydrogen ions back through .inhibitors of electron transport chain ppt (PPT) Chapter 6 Electron transport chain and In oxidative phosphorylation, the electron transfer potential of NADH and FADH2 is converted into the phosphoryl transfer potential of ATP. The standard reduction potential (E0) is a quantitative measure of the ease with which a compound can be reduced; or how readily it accepts electrons. The more positive the E0, the more readily the compound .
1. Introduction. Complex I is a very large enzyme catalyzing at the entry point of the mitochondrial electron transport chain [1–3].The total number of subunits in the bovine heart enzyme is 45 [] for a molecular mass of about 1000 KDa.Seven subunits are products of the mitochondrial genome [5,6] that correspond to hydrophobic subunits named . Electrons are passed down an electrochemical gradient, and molecular oxygen is the final electron acceptor (molecular oxygen). There are site specific inhibitors of the ETC to be aware of, and these will disrupt electron flow reducing overall ATP production. Figure 4.14: Overview of the electron transport chain (ETC).The electron transport chain is a collection of membrane-embedded proteins and organic molecules, most of them organized into four large complexes labeled I to IV. In eukaryotes, many copies of these molecules are found in the inner mitochondrial membrane. In prokaryotes, the electron transport chain components are found in the plasma . Biochemistry Electron transport chain. The document summarizes electron transport chain (ETC) and ATP synthase. It describes: 1) ETC consists of 5 complexes (I-IV and V) in the mitochondria that transport electrons from nutrients to oxygen, pumping protons out and building up a proton gradient. 2) Complexes I, III, and . The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named .Colby College offers a PowerPoint presentation on the electron transport chain, a crucial process in cellular respiration and energy production. Learn about the components, mechanisms, and regulation of this complex system with clear diagrams and explanations. The electron transport chain (ETC) is a group of proteins and organic molecules found in the inner membrane of mitochondria. Each chain member transfers electrons in a series of oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions to form a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis. The importance of ETC is that it is the primary source of ATP .
Chemicals can induce adverse effects in humans by inhibiting mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) such as disrupting mitochondrial membrane potential, enhancing oxidative stress and causing some diseases. Thus, identifying ETC inhibitors (ETCi) is important to chemical risk assessment and protecting the public health.
The mitochondrial electron transport chain utilizes a series of electron transfer reactions to generate cellular ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. A consequence of electron transfer is the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which contributes to both homeostatic signaling as well as oxidative stress during .
Electron Transport Chain.ppt. The electron transport chain is the final pathway where electrons from nutrients are transferred to oxygen to form water. Electrons enter the chain from NADH or FADH2 and are passed through four complexes and coenzyme Q, which pump protons out of the mitochondrial matrix. This creates a proton .Hydrogen Sulphide: It is a respiratory inhibitor which blocks the complex IV of the electron transport chain. It is toxic. Inhibitors of ATP synthase complex (Phosphorylation inhibitor) These inhibitors prevent the synthesis of ATP by binding to the ATP synthase complex. It prevents the inflow of protons. New drug targets include various enzymes in the electron transport pathway that are critical for maintaining growth and survival of the causative bacterium. Following approval of the ATP synthase .
inhibitors of electron transport chain ppt|(PPT) Chapter 6 Electron transport chain and
PH0 · PowerPoint Presentation
PH1 · PPT
PH2 · Inhibitors of Electron Transport Chain – Metabolism of
PH3 · INHIBITORS OF ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN AND
PH4 · INHIBITORS AND UNCOUPLERS IN ELECTRONE
PH5 · Electron transport chain
PH6 · Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation
PH7 · Colby College
PH8 · 4.3: Electron transport chain (ETC)
PH9 · (PPT) Chapter 6 Electron transport chain and